Integrated Rate Law for Zero and First Order Reactions
Integrated Rate Law for Zero and First Order Reactions: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Zero Order Reactions, Integrated Rate Equation for Zero Order Reactions, Half Life Period for Zero Order Reactions, Time-Concentration Graph for Zero Order Reactions, etc.
Important Questions on Integrated Rate Law for Zero and First Order Reactions
A first order reaction is complete in minute. Calculate the time taken for the reaction to be complete:
,
In a first-order reaction, the concentration of reactant decreases from in. The rate constant of reaction in is
For a zero-order reaction, with the initial reactant concentration , the time for completion of the reaction is:
Which of the following is incorrect?
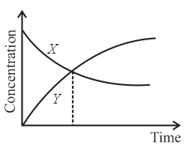
The accompanying figure depicts the change in concentration of species and for the elementary reaction as a function of time. The point of intersection of two curves represents:
The order of a reaction for which a linear line (with a negative slope) is obtained in a graph of vs is:
Two-third life for a first-order reaction is minutes. The value of its velocity constant is nearly
The time taken for the completion of three-fourths of a first-order reaction is
The half-life period for a zero order reaction is equal to:
Show that, In a first order reaction, time required for completion of is _____ times of half life. ().
The half-life period of a zero order reaction product is given by:
A first order reaction has reaction constant, . The half-life of the reaction in seconds is: _____
A reaction occurs by the following mechanism:
(i)
(ii)
The net reaction is:
The half life of first order reaction is hours. Time take (in hours) for the concentration of reactant to decrease from to is:
A first order reaction takes minutes for decomposition. Calculate half life?
Rate constant of a chemical reaction is . Calculate the order of reaction?
What is the mathematical relation between half life of zero order reaction and its rate constant.
The half-life is the time in which the concentration of the reactant is reduced to half of its initial concentration.
The reaction is a first order gas reaction with . What percentage of is decomposed on heating this gas for ?
For next two question please follow the same
In a vessel gaseous dimethyl ether at initial pressure 'p0' atm. Dimethyl ether decomposes on heating as per the reaction by first order kinetics.
It is observed that the half-life period for this reaction is 0.2 h. After a very long time, pressure in the vessel is observed to be 1.2 atm. Assume ideal behaviour of all gases with constant V-T conditions.
What would be the approximate pressure in the vessel at 0.6 h ?
